10 Simple Steps to Test Oxygen Levels in Your Fish Tank
To test oxygen levels in a fish tank, use an aquarium test kit. Avoid overcrowding and overfeeding your fish to maintain proper oxygen levels.
Oxygen is crucial to the survival of fish in an aquarium. Fish breathe oxygen through their gills, and a lack of oxygen in their water can be fatal. Therefore, it is essential to monitor the oxygen levels regularly in your fish tank.
In this article, we will discuss how to test oxygen levels in your aquarium, the signs of low oxygen levels, and ways to maintain a healthy oxygen balance in your fish tank. By following these tips, you can help ensure the health and well-being of your aquarium pets.

Credit: www.tfhmagazine.com
Understanding The Importance Of Oxygen Levels In Your Fish Tank
Why Oxygen Is Important For Your Fish
Your fish depend on oxygen to breathe, just like humans. Oxygen levels in your fish tank are vital for the health of your aquatic pets. Here are some reasons why oxygen is essential to your fish:
- Oxygen helps your fish convert food into energy and grow.
- Adequate oxygen levels in water support the growth of beneficial bacteria, which break down harmful substances such as ammonia and nitrite.
- Proper oxygen levels in water help prevent the buildup of toxins, which can make your fish sick.
The Risks Of Low Oxygen Levels
If the oxygen levels in your fish tank are too low, it can be harmful to your fish. When your pet fish don’t get enough oxygen, they may show the following symptoms:
- Gasping for air at the surface of the water.
- Lethargy and slower swimming.
- Loss of appetite and unusual behavior.
Low oxygen levels in the water can be caused by insufficient surface agitation, overstocking your tank, and using a filter that is too strong for the size of your tank.
The Consequences Of High Oxygen Levels
Though less common than low oxygen levels, high oxygen levels in your fish tank can also cause problems. Here are some possible side effects of too much oxygen in your aquarium water:
- Hyperactivity and increased swimming.
- Fish gasping at the surface, showing signs of stress.
- Damage to the gills of your fish, resulting in respiratory issues.
High oxygen levels in water are usually caused by using too much aeration, agitation, or oxygenation methods.
Maintaining the right amount of oxygen in your fish tank is essential to the health of your aquatic pets. Keeping up with regular water changes, adding live plants, and keeping an eye on your fish’s behavior can help ensure that your fish stay healthy and happy.
Gathering The Equipment Needed
Understanding The Basic Requirements
Before testing the oxygen levels in your fish tank, it’s essential to know the basics requirements to avoid any possible errors. Here are the fundamental aspects you need to keep in mind:
- A fish tank aerator or filter is necessary for maintaining proper oxygen levels.
- The ideal oxygen level in a fish tank is between 5-6 mg/l, while anything less than 2 mg/l is potentially harmful to fish.
- The oxygen level is also affected by factors such as temperature, water movement, and the number of fish in the tank.
Choosing The Right Test Kit
To test oxygen levels in your fish tank, you need to have the correct testing kit. Here are some essential things to consider when selecting a test kit:
- There are different types of oxygen test kits, including test strips, colorimeters and electronic probes.
- Test strips are the easiest to use but are not as accurate as the other types.
- Colorimeters can provide accurate results but may require a considerable investment. Electronic probes are the most accurate but are also the priciest.
Additional Equipment Needed For Accurate Results
Besides a test kit, there are other essential items you need for accurate results. Here are some critical things you need to get:
- A standard thermometer to measure water temperature is essential because temperature affects oxygen solubility in water.
- A stopwatch or timer is vital to monitor the time needed for the test.
- A white tray is also useful because you need a flat, white surface to perform the test accurately.
By understanding the basic requirements for testing oxygen levels in fish tanks, choosing the right test kit and gathering the proper equipment, you can ensure that your fish stay healthy and happy.
Preparing Your Fish Tank For Testing
Testing the oxygen levels in your fish tank is essential in maintaining the health and well-being of your aquatic pets. Before you start testing, it is important to prepare your fish tank adequately. In this section, we’ll discuss some important things to consider before testing, as well as cleaning and rinsing your test kit and equipment, and preparing your fish tank for testing.
Things To Consider Before Testing:
- Make sure you have a reliable test kit that measures both oxygen and ph levels in the water.
- Allow enough time for your fish to acclimate to any changes in the water before testing.
- Avoid testing right after cleaning your tank or adding new fish, plants, or decorations.
- Test oxygen levels at different times of day to ensure accuracy.
Cleaning And Rinsing Your Test Kit And Equipment:
- Rinse your test tubes and other equipment with distilled water, to avoid any contamination from tap water.
- Make sure to dry all equipment thoroughly, as any moisture can interfere with the accuracy of your results.
Preparing The Fish Tank For Testing:
- Turn off any air pumps and filters for at least an hour before taking a reading.
- Avoid disturbing the water by agitating it with a net or your hand, as this may alter the oxygen levels.
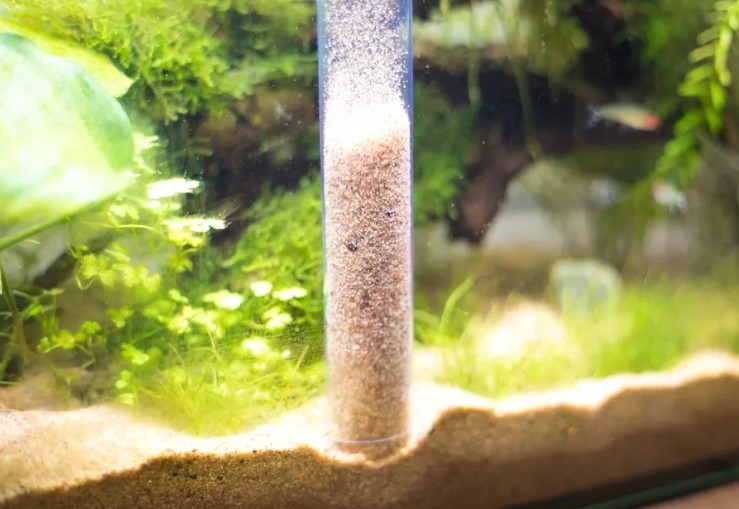
- Place the test tube at a depth of at least six inches in the water.
- Fill the test tube accurately to the marked line with water from your fish tank.
- Add the reagents to the water in the test tube as per the instructions provided with your test kit, and gently shake the tube.
- Wait for the color of the water to change completely, and match the color of the water with the key provided.
With these tips, you should be able to prepare your fish tank for testing and get an accurate reading of the oxygen levels in your aquatic habitat. Remember, testing regularly can help ensure the longevity of your aquatic pets.
Performing The Oxygen Level Test
Testing the oxygen levels in your fish tank is an essential part of keeping your fish healthy and happy. Performing an oxygen level test is easy, and in this section, we’ll take you through the process step-by-step.
Step-By-Step Instructions On How To Perform A Test
- Turn off any air pumps or other sources of aeration. Let the tank sit for at least a half-hour before beginning the test.
- Fill the test tube (included in most test kits) to the line with water from the tank.
- Add the reagent to the test tube according to the instructions in your kit.
- Let the test tube sit for the designated amount of time, depending on which kit you’re using.
- Compare the resulting color of the water with the chart provided in the test kit.
Tips For Accurate Results
Here are some tips to keep in mind to ensure you get accurate results from your oxygen level test:
- Always follow the instructions provided with your kit.
- Take the test at the same time each day, as oxygen levels can fluctuate throughout the day.
- Test the water in multiple places throughout the tank, as oxygen levels aren’t consistent throughout.
Examples Of Test Results
Test results will vary depending on many factors, including the type of test kit you’re using, the size of your tank, and the types and number of fish you have. However, there are some general guidelines you can follow:
- Oxygen levels should be at least 5 mg/l for fish to be healthy.
- If your test indicates levels below 4 mg/l, immediately perform a water change and investigate the cause of low oxygen levels.
- In some cases, oxygen levels may be too high, which can also be harmful to fish. Levels above 12 mg/l are dangerous and can cause fish to suffocate.
Performing an oxygen level test is quick and easy, and doing so regularly can help keep your fish healthy and happy. Remember to follow the instructions in your kit and take readings at the same time each day for the best results.
Analyzing And Interpreting Oxygen Test Results
Testing oxygen levels in your fish tank is an essential aspect of maintaining a healthy and thriving aquatic environment for your fish and plants. Analyzing the test results correctly and interpreting them accurately can go a long way in ensuring that your fish and plants are in good health.
In this section, we will explore how to understand, analyze, and interpret oxygen test results to keep your fish tank healthy.
Understanding The Reading On The Test Kit
To analyze and interpret the oxygen test results correctly, we need to understand the reading on the test kit. Oxygen test kits for fish tanks usually come with a color chart that helps you determine the oxygen levels in your tank.
Here are some key points to keep in mind:
- The test kit’s color chart comes with a series of color blocks that correspond to different oxygen levels.
- The color of the water in your test tube will change based on the oxygen levels in your tank.
- Compare the color of the water in your test tube with the color blocks on the chart to determine the oxygen levels in your tank.
Normal Oxygen Levels For Fish And Plants
The next step in analyzing and interpreting oxygen test results is to understand normal oxygen levels for fish and plants. Oxygen levels within the range of 5 to 7 milligrams per liter (mg/l) are ideal for most fish species and aquarium plants.
Some fish species may require higher oxygen levels, while others may tolerate lower oxygen levels. Here’s what you need to know:
- Fish and plants depend on dissolved oxygen to survive. Adequate oxygen levels are crucial for their respiration.
- Normal oxygen levels in a fish tank should range from 5-7 mg/l.
- For some fish species that require more oxygen, you may want to maintain oxygen levels of up to 8-9 mg/l.
- It’s important to note that too much oxygen can be as harmful as too little oxygen.
Interpreting High Or Low Oxygen Levels
Interpreting high or low oxygen levels is the final step in analyzing and interpreting oxygen test results. Here are some things to keep in mind:
Low Oxygen Levels
- If the oxygen levels in your tank are low (below 5 mg/l), it can be harmful to your fish and plants.
- Low oxygen levels can be caused by overcrowding, warm temperatures, lack of agitation, and overfeeding.
- Signs of low oxygen levels include lethargic fish, gasping for air at the surface, and poor plant growth.
- To increase oxygen levels, you can increase surface agitation, reduce feeding, improve water circulation, add an air stone, or perform a partial water change.
High Oxygen Levels
- High oxygen levels can also be harmful to your fish and plants.
- Too much oxygen can cause stress to your fish and damage their gills.
- Signs of high oxygen levels include fish gasping at the surface, hyperactivity, and irregular breathing.
- To reduce oxygen levels, you can reduce surface agitation, decrease the water’s flow rate, or add plants that absorb oxygen.
Analyzing and interpreting oxygen test results is an essential aspect of maintaining a healthy and thriving aquarium. Understanding the reading on the test kit, knowing the normal oxygen levels for your fish and plants, and interpreting high or low oxygen levels can help you keep your fish and plants healthy and happy.
Adjusting Oxygen Levels In Your Fish Tank
Maintaining healthy oxygen levels in your fish tank is essential for your fish’s survival. When oxygen levels fall too low, fish become stressed, and in extreme cases, they can suffocate. Here are some methods to help you adjust oxygen levels in your fish tank:
Common Methods For Increasing Oxygen Levels
Several methods are available to increase oxygen levels in your fish tank. Here are some common ones:
- Air pump and air stone: An air pump and air stone can increase water agitation, increasing oxygen transfer into the water.
- Increasing surface area: Increasing the water’s surface area can bolster oxygen transfer. You can add an aquarium ornament or increase movement from a filter to accomplish this.
- Reduce bioload: Too many fish or overfeeding can cause low oxygen levels. Reduce the bioload or reduce feeding to help manage oxygen levels.
Root Causes Of Low Oxygen Levels And How To Address Them
Several things can cause low oxygen levels in fish tanks. Here are some causes and how to address them:
- Poor water circulation: Poor water circulation can prevent oxygen distribution throughout the water. Ensure your filter is functioning correctly. Consider adding a powerhead or additional filter.
- High water temperature: Warm water holds less oxygen than cold water, so high temperatures can reduce oxygen levels. Maintain recommended temperatures.
- Low water levels: Low water levels can limit oxygen exchange from the air. Check the water levels regularly and top off as needed.
- Dirty substrate and decor: Dirty substrates and decor can reduce oxygen levels in the water column. Clean them regularly to ensure good water flow.
- Overcrowding: An overcrowded tank can quickly consume all the oxygen, leading to low oxygen levels. Reduce the number of fish in your tank.
How To Balance Oxygen Levels With Other Aquarium Parameters
While oxygen levels are crucial to fish health, balancing other parameters is also essential. Here are some other factors to consider when balancing oxygen levels:
- Ph levels: Low or high ph levels can affect oxygen solubility. Keep ph levels in the recommended range.
- Ammonia levels: High levels of ammonia can reduce oxygen uptake. Monitor ammonia levels and perform necessary water changes.
- Water hardness: Water hardness can affect oxygen solubility. Keep water hardness in the recommended range.
- Water temperature: Coldwater can hold more oxygen than warm water. Maintain recommended temperatures.
Remember, too little oxygen in your fish tank can harm your fish, and too much oxygen can negatively impact ph levels. Test your oxygen levels regularly and adjust the parameters to keep your fish healthy.
Frequently Asked Questions For How To Test Oxygen Levels In Fish Tank
How Do I Test Oxygen Levels In A Fish Tank?
Using an oxygen test kit with a dropper, fill the vial and add reagent drops. Shake and wait for the color to develop, then compare to the chart.
How Often Should I Test Oxygen Levels In My Fish Tank?
Test your fish tank’s oxygen level at least once a week, especially during hot weather or if you have an overcrowded tank.
What Factors Can Affect Oxygen Levels In A Fish Tank?
Overcrowding, but also things such as high temperatures, decaying matter, reduced surface agitation, or a dirty filter will lower oxygen levels.
How Can I Increase Oxygen Levels In My Fish Tank?
Increasing surface agitation, adding an air pump, or adding live plants to your aquarium can help oxygenate your fish tank. Additionally, regularly cleaning your filter and removing excess waste can help as well.
Conclusion
After reading this comprehensive guide, you are now equipped with the necessary knowledge and tools to test oxygen levels in your fish tank. Remember, maintaining an optimal oxygen level is crucial for the health and wellbeing of your aquatic pets.
Testing your tank’s oxygen levels regularly will help you identify and rectify any issues before they become harmful. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can ensure that your fish and plants thrive in a healthy and balanced ecosystem.
Always make it a priority to provide the right environment for your pets, and you’ll enjoy watching them flourish for years to come. Don’t forget to share this information with your friends who also have fish tanks, and encourage them to test their oxygen levels regularly.